What Causes Bleeding Gums? Understanding the Factors and Solutions
Contents
- The Importance of Healthy Gums for Oral Health
- What Causes Bleeding Gums?
- The Importance of Professional Dental Care and Regular Check-ups
- Conclusion:
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Gum Disease: A Common Culprit Behind Bleeding Gums
- 2. Poor Oral Hygiene Habits: Ignoring the Basics
- 3. Hormonal Changes and Bleeding Gums: Exploring the Connection:
- 4. Nutritional Deficiencies and Gum Health: Key Factors:
- 5. Medications and Bleeding Gums: Unintended Side Effects:
- 6. Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and Stress as Contributors:
- 7. Systemic Conditions and Bleeding Gums: An Overview:
- 8. Dental Procedures and Temporary Gum Sensitivity:
Gum bleeding can be unsettling and uncomfortable. Although it's a widespread problem, recognising the fundamental causes is essential for finding a solution.
In this blog, we will explore various factors that contribute to bleeding gums, from poor oral hygiene habits to hormonal changes, medications, and systemic conditions.
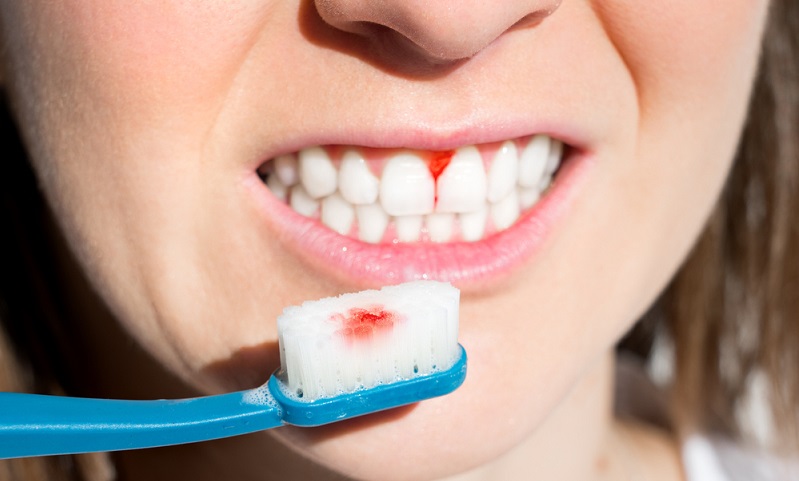
By identifying these causes and implementing appropriate solutions, you can take proactive steps towards achieving healthier gums and a confident smile.
The Importance of Healthy Gums for Oral Health
Before delving into the causes of bleeding gums, let's first understand the significance of gum health. Your gums play a vital role in supporting your teeth, protecting the underlying bone, and maintaining overall oral health.
Healthy gums are firm, and pale pink, and do not bleed during routine brushing or flossing. When gums become inflamed and start to bleed, it is often a sign of an underlying issue that needs attention.
What Causes Bleeding Gums?
1. Gum Disease: A Common Culprit Behind Bleeding Gums
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a leading cause of bleeding gums. It occurs when the gum tissues become infected due to the accumulation of plaque and tartar.
Bacteria in the mouth release toxins that irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and bleeding. If left untreated, gum disease can progress to more severe stages and result in tooth loss.
Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene are essential for preventing and managing gum disease.
2. Poor Oral Hygiene Habits: Ignoring the Basics
Neglecting proper oral hygiene practices is a significant factor in the development of bleeding gums. Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up along the gum line, leading to gum inflammation and bleeding.
It is essential to brush at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Additionally, flossing daily helps remove plaque and debris from between the teeth and along the gumline, promoting healthier gums.
3. Hormonal Changes and Bleeding Gums: Exploring the Connection:
Hormonal changes in the body, such as during pregnancy or puberty, can contribute to bleeding gums. The surge in hormone levels can make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
This condition, known as pregnancy gingivitis or hormonal gingivitis, can cause bleeding and tenderness in the gums.
Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental visits are crucial during these periods to manage the symptoms of gingivitis and prevent further complications.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies and Gum Health: Key Factors:
A balanced diet plays a vital role in maintaining healthy gums. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in vitamin C and vitamin K, can weaken gum tissues and lead to bleeding gums.
When it comes to maintaining healthy gums, vitamin C and vitamin K both play important roles in collagen formation and blood clotting. Your diet can support gum health if you include a variety of fruits, vegetables, and nutrient-rich meals.
5. Medications and Bleeding Gums: Unintended Side Effects:
Gum bleeding is made more likely by several drugs, including antiplatelet and blood thinners. These medications are essential for treating a variety of medical issues, but they may prevent blood from clotting properly.
If you are taking medications that contribute to bleeding gums, it is important to inform your dentist, who can provide guidance on preventive measures and suitable oral care practices.
6. Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and Stress as Contributors:
Smoking is not only detrimental to overall health but also significantly impacts gum health.
Smoking weakens the immune system, restricts blood flow to the gums, and hinders the healing process, making smokers more susceptible to gum disease and bleeding gums.
Stress is another lifestyle factor that can affect gum health. Chronic stress weakens the immune system and makes it harder for the body to fight off infections, including gum disease.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and seeking support can help reduce the risk of bleeding gums.
7. Systemic Conditions and Bleeding Gums: An Overview:
Certain systemic conditions, such as diabetes and leukaemia, can increase the likelihood of bleeding gums. Diabetes affects the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels and can impair gum healing.
Leukaemia, a type of blood cancer, can manifest as bleeding gums due to the reduced ability of blood to clot properly.
If you have a systemic condition, it is crucial to work closely with your healthcare team and dentist to manage your oral health effectively.
8. Dental Procedures and Temporary Gum Sensitivity:
Some dental procedures, such as deep cleanings or scaling and root planing, may cause temporary gum sensitivity and bleeding.
These procedures are often necessary for treating gum disease and restoring gum health.
Your dentist will provide instructions on proper aftercare, including gentle brushing and avoiding certain foods or activities that may exacerbate gum sensitivity.
Taking Action: Tips for Preventing and Treating Bleeding Gums
Maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily.
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush: A soft brush minimizes irritation to the gums.
Consider an antimicrobial mouthwash: Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and promote gum health.
Eat a balanced diet: Include foods rich in vitamins and minerals necessary for gum health.
Quit smoking: Seek support and resources to quit smoking and improve your gum health.
Manage stress: Incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine.
Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain saliva production, which aids in oral health.
Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups allow early detection and treatment of gum problems.
The Importance of Professional Dental Care and Regular Check-ups
While home care is crucial, professional dental care is equally important in maintaining gum health.
Regular check-ups allow your dentist to monitor your gum health, provide professional cleanings, and address any underlying issues promptly.
Your dentist can also provide personalized recommendations and guidance based on your specific oral health needs.
Conclusion:
Gum disease, bad dental hygiene, hormonal shifts, and systemic disorders are just a few of the underlying conditions that can manifest as bleeding gums.
You may take charge of your gum health by being aware of the causes and taking preventive actions, such as practising excellent oral hygiene, leading a healthy lifestyle, and getting professional dental care.
Remember that maintaining your smile and achieving excellent dental health depends on early identification and prompt treatment. Consult your dentist for a thorough evaluation if you have persistent or severe bleeding gums.
Frequently Asked Questions
What autoimmune diseases cause bleeding gums?
Several autoimmune diseases can contribute to bleeding gums, including:
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): SLE can cause oral manifestations, including gum inflammation and bleeding.
Sjögren's Syndrome: This autoimmune disorder affects the salivary glands, leading to dry mouth and increased vulnerability to gum problems.
Behçet's Disease: This rare autoimmune condition can cause oral ulcers and inflammation, which may result in bleeding gums.
What causes gums to bleed?
There are several causes of bleeding gums, such as:
Gum Disease: The primary cause of bleeding gums is gum disease or periodontal disease, resulting from plaque buildup and bacterial infection.
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing habits can lead to plaque accumulation, gum inflammation, and bleeding.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menstruation, or puberty can make gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding.
Vitamin Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins C and K can weaken gum tissues and contribute to bleeding.
Medications: Certain medications, like blood thinners, can interfere with blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding gums.
Trauma or Injury: Accidental injury to the gums, harsh brushing, or using improper dental tools can cause gum bleeding.
Systemic Conditions: Some systemic diseases, like leukaemia or blood disorders, may cause bleeding gums as a symptom.
What vitamin deficiency causes bleeding gums?
A deficiency in vitamin C can lead to bleeding gums. Vitamin C is essential for maintaining healthy gum tissues, and insufficient intake can weaken blood vessels, making the gums more prone to bleeding.
Vitamin K deficiency can cause gums to bleed. Vitamin K plays a vital role in blood clotting, and its deficiency can impair the clotting process, leading to bleeding gums.
What causes bleeding gums when brushing teeth?
Bleeding gums during brushing can be caused by various factors, including:
Gingivitis: The initial stage of gum disease characterized by gum inflammation and bleeding.
Plaque Accumulation: Insufficient oral hygiene practices can result in plaque buildup, which irritates the gums and leads to bleeding.
Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard or using a toothbrush with hard bristles can damage the delicate gum tissues, causing them to bleed.
Gum Sensitivity: Some individuals naturally have more sensitive gums, and even gentle brushing can cause mild bleeding.
What causes bleeding gums when flossing?
Bleeding gums during flossing can occur due to the following:
Gingivitis or Gum Disease: Inflamed gums are more susceptible to bleeding, especially when flossing disrupts the plaque and bacteria along the gumline.
Inadequate Flossing Technique: Incorrect flossing techniques, such as snapping the floss forcefully into the gums, can cause bleeding.
Infrequent Flossing: If you haven't flossed regularly, the gums may be more sensitive and prone to bleeding initially. With consistent flossing, bleeding should decrease over time.
What disease causes bleeding gums?
Gum disease or periodontal disease is a common condition that causes bleeding gums.
However, bleeding gums can also be a symptom of systemic conditions such as leukaemia, scurvy (severe vitamin C deficiency), or other blood disorders.
If you are experiencing persistent bleeding gums, it is essential to consult with a dentist or healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.