Jaw Cancer - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Survival Rate in India
Contents
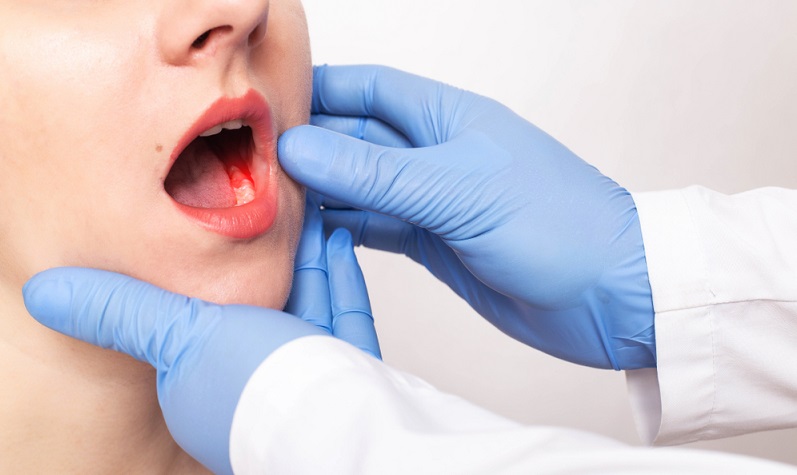
Symptoms of Jaw Cancer
As with many early stages of cancer, early signs may be imperceptible. Because oral cancer sometimes precedes jaw cancer, some early symptoms may include:
white or red spot on the gums, tongue, or mouth lining blood or discomfort in the mouth jaw growth or swelling
As the cancer develops into the jaw, the following symptoms may become more noticeable:
- Pain with swallowing
- Bulge in the neck and ear pain
- Changes in speech
- Mouth sores that do not heal after 3 weeks
What are the Causes of Jaw Cancer?
Jaw cancer (mandibular or hard palate) is caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors, while specific risk factors can enhance your risk of developing the condition.
These are some of the risk factors:
1. Tobacco:
The most common risk factor for both hard palate and mandibular malignancies is smoking or chewing tobacco.
People who chew betel nut, a seed from the areca tree, are more likely to acquire jaw cancer.
2. Excessive alcohol drinking:
It raises the risk of oral squamous cell carcinoma; smoking combined with excessive alcohol consumption nearly doubles the risk.
3. Excess weight:
Being overweight increases the risk of oropharyngeal and laryngeal malignancies.
4. Age:
People over the age of 55 are more likely to develop oral cavity and oropharyngeal malignancies.
5. Poor oral hygiene:
Although research is ongoing, the health of your mouth and gums may be a factor in the development of oral cavity and oropharyngeal malignancies.
6. Infections:
Viral infections, such as HPV, increase the probability of incidence in adults under the age of 50.
7. Poor Diet:
A diet poor in fruits and vegetables raises the risk of oral cavity and oropharynx cancer.
Jaw Cancer Treatments
The quick answer is yes. The type of treatment you receive will be determined by the location and extent of your cancer, as well as the stage.
The most common initial treatment for oral cavity malignancies is surgery, however, radiation and/or chemotherapy may also be alternatives.
1. Surgery
Doctors aim to remove the tumor unless you are too sick to have surgery or surgery is not an acceptable therapy choice for you.
The sort of surgery required is determined by the location of the tumour.
A maxillectomy, or removal of a portion of the maxilla, or bone that forms the roof of the mouth, may be part of hard palate surgery.
A mandibulectomy, or surgery to remove a portion of the lower jaw, is one type of mandibular surgery.
2. Radiation Treatment
Radiation therapy is frequently indicated following surgery for both hard palate and mandibular malignancies.
Adjuvant radiation is used to prevent tumor recurrence if the tumor could not be entirely removed surgically or if the cancer spreads to lymph nodes, nerves, or blood vessels.
Radiation therapy may also be used to treat aggressive or advanced-stage malignancies.
3. Chemotherapy
Though chemotherapy is not often used to treat jaw cancer, it may be administered in conjunction with adjuvant radiation therapy if cancer has spread from lymph nodes to surrounding tissues or lingers after surgery.
Can You Get Cancer In Your Jaw?
Jaw cancer is an uncommon kind of head and neck cancer that is also one of several types of oral cancer.
According to the American Society of Clinical Oncology, different head and neck malignancies account for around 4% of all cancers in the United States.
Most commonly, jaw cancer arises when tumors in the head and neck spread to the floor of the mouth, tongue, tonsils, salivary glands, or palate.
Rarely, jaw cancer can develop on its own as osteosarcoma, a type of bone cancer.
Jaw cancer can occur in either the upper or lower jaw:
- Mandibular cancer is a type of jaw cancer that develops in the lower region of the jaw, known as the mandible.
- Hard palate cancer occurs when jaw cancer occurs in the upper jaw region or maxilla.
Can Jaw Cancer Cause Tooth Pain?
Jawbone tumors, including malignant ones like squamous cell carcinoma, can cause unusual tooth movement and discomfort.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Tooth Movement:
Tumors in the jawbone can lead to unexplained tooth movement or looseness. If you notice your teeth becoming loose or shifting unexpectedly, it could be a sign of a tumor affecting the jawbone. - Types of Tumors:
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of malignant jaw cancer that invades the jawbone through the tooth sockets. - Other Symptoms:
In addition to tooth mobility, symptoms like jaw discomfort, swelling, lumps on the jaw, or loose teeth might indicate jaw cancer, though they can also be signs of other oral conditions. - Seek Immediate Evaluation:
If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your dentist promptly for a thorough examination and screening. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
Is Jaw Pain A Symptom Of Cancer?
Jaw pain can be a symptom of jaw cancer, though it's important to consider other potential causes as well.
Here’s what you should know:
- Jaw Pain and Tumors:
Jaw tumors, while rare and often benign, can be aggressive and spread to surrounding bone and tissue. This may result in tooth displacement and persistent pain. - Consult Your Dentist:
If you experience unexplained jaw pain, it’s crucial to consult your dentist rather than assuming it's just a toothache. Early evaluation can help determine the cause and ensure timely treatment. - Other Possible Causes:
Keep in mind that jaw pain could also be related to issues like TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders, which are different from cancer but still require attention. - Imaging and Diagnosis:
If a tumor is suspected, your dentist will likely recommend imaging tests to examine your jaw more closely. A biopsy may be ordered if a tumor is detected, to confirm the diagnosis and plan the appropriate treatment.
Survival Rates for Jaw Cancer
There are no available survival rates by stage or for jaw cancer in particular.
The research found that the five-year relative survival rate for malignancies of the gums and other areas of the mouth, including the jaw, is 60%.
Final Outlook
Certain persons are more likely to survive jaw bone cancer. This includes the following:
- Having no other health issues who had their tumor removed and whose cancer had not spread to their lymph nodes
- Patients who have had their jaw bone cancer surgically removed have an overall 5-year survival rate of roughly 88%.
- In comparison, 26.6% of people did not have the tumor surgically removed.
- Jaw cancer is a relatively uncommon type of head and neck cancer. Jaw cancer frequently begins in the mouth before spreading to the jaw.
- Tobacco and alcohol usage, in particular, can raise your chances of having this cancer.
- Symptoms do not normally appear in early-stage cancer, but as the disease advances, different symptoms may appear.
- Surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy are common treatments.
- The specific treatment plan is determined by the type of jaw cancer and how far it has spread.